Revolutionizing Eye Care: How Tele-Ophthalmology is Breaking Down Barriers to Access

Over the past couple of years, the global healthcare landscape has been undergoing significant transformation due to new technologies and increased demand for accessible health care services. One of the major breakthroughs is in ophthalmology, where tele-ophthalmology is enabling eye care to reach patients wherever they are. Until recently, eye health was the domain of in-person consultations and diagnostic procedures, but that is changing with remote consultations, real-time diagnostics, and high-quality imaging.
Tele-Ophthalmology aims to break geographical barriers and helps provide eye care anytime, anywhere—especially to underserved populations. It helps detect eye conditions early, improves patient experience, and relieves the burden on healthcare systems through telemedicine technology. In this blog post, we will shed light on how tele-ophthalmology is transforming eye care by making it accessible in all areas and providing high-quality results without compromising on care.
1. The Rising Demand For Affordable Eye Health Care
Cataracts, glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, and age-related macular degeneration (AMD) are major eye diseases and significant causes of visual impairment worldwide. In India alone, millions suffer from such conditions, with many rural or underserved areas lacking even a single specialist.
These populations struggle to access traditional in-person eye care due to logistical concerns, a lack of ophthalmologists, and the time and expense associated with traveling for consultations. Tele-ophthalmology can address these challenges by providing specialized eye care services from the safety, convenience, and comfort of patients’ homes, ensuring quality healthcare reaches everyone, no matter their location.
2. What is Tele-Ophthalmology?
Tele-ophthalmology is the practice of delivering eye care remotely using modern telemedicine technology. This may involve video consultations, diagnostic scans, and post-diagnosis follow-ups through a blend of video conferencing, mobile apps, and deep learning image analytics. Patients can remotely engage with ophthalmologists, provide their medical history, and even access eye screenings through tele-ophthalmology platforms from the comfort of their homes.
Tele-ophthalmology is highly modular, adapting to the needs of each case:
Screening and Early Detection: Regular eye screenings are essential for detecting and treating conditions like glaucoma or diabetic retinopathy before symptoms appear. Through advanced imaging technology, these issues can now be screened without any in-person contact, leading to earlier detection.
Remote Consultations: Patients in remote areas no longer need to travel long distances for consultations. Tele-ophthalmology allows them to meet with an ophthalmologist online and receive expert advice instantly.
Post-Operative Follow-Up: Tele-ophthalmology helps reduce the number of physical follow-up visits after surgery, with many of them now scheduled online through virtual check-ups.
3. Tele-Ophthalmology to Improve Access to Care
The primary role of tele-ophthalmology is to enhance existing services by extending care to regions with low specialist access. Here’s how tele-ophthalmology is improving access:
Reaching Hard-to-Reach Areas: In many rural areas across the globe, particularly in India, there is a critical shortage of ophthalmologists. Tele-ophthalmology helps mitigate these geographical barriers, connecting patients in remote locations to specialists in urban centers.
Reducing Travel and Costs: Elderly patients or those who have difficulty traveling can consult specialists from the comfort of their homes. This reduces travel time and costs, easing the burden on patients and their families.
4. How Tele-Ophthalmology Technology Works
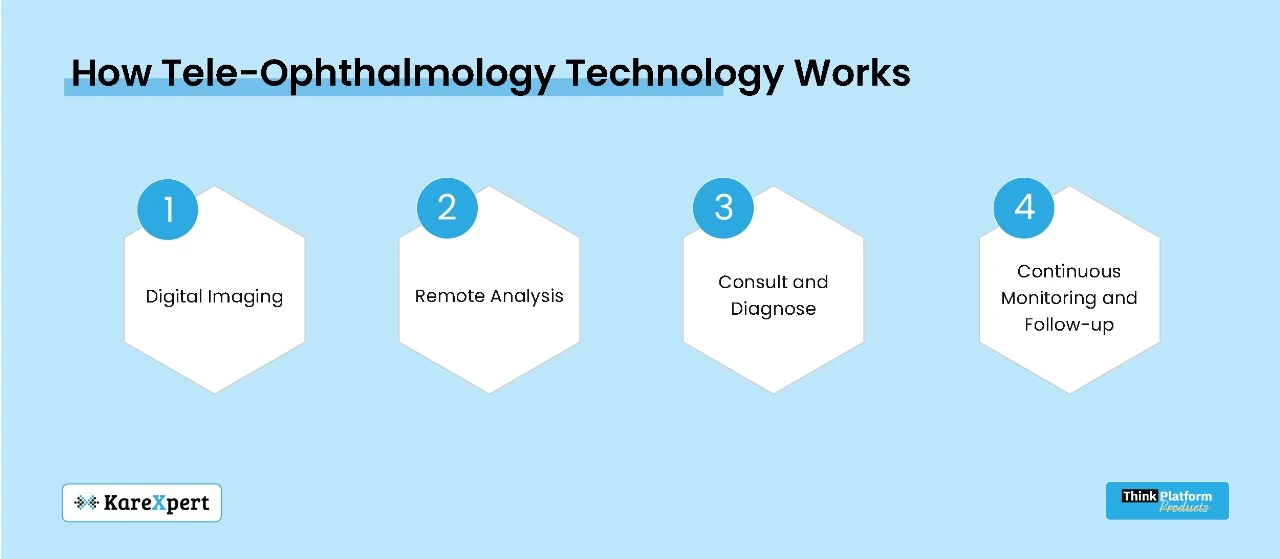
Tele-ophthalmology integrates various technologies to deliver complete eye care services from a distance. These include high-definition cameras, digital imaging tools, cloud-enabled storage, and secure video conferencing. Here’s how the process works:
Step 1: Digital Imaging
Patients can take digital eye exams at a local clinic or from home using an internet-connected device. Digital fundus cameras or slit-lamp imaging devices capture high-resolution images, which are uploaded to a secure cloud platform.
Step 2: Remote Analysis
Ophthalmologists review the data remotely, with advanced algorithms speeding up the process by helping healthcare professionals detect issues more easily.
Step 3: Consult and Diagnose
Based on the imaging results and patient history, the ophthalmologist conducts a tele-consultation, diagnosing the patient and recommending treatment or referring them for in-person care if necessary.
Step 4: Continuous Monitoring and Follow-up
In chronic conditions like glaucoma, which require regular follow-ups, tele-ophthalmology can facilitate continuous monitoring through mobile apps that allow patients to track their progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
5. Challenges in Tele-Ophthalmology
While tele-ophthalmology offers significant advantages, it also faces challenges such as data security, diagnostic accuracy, and technological literacy among patients. Here’s how these challenges can be addressed:
Ensuring Data Security: Tele-ophthalmology platforms must comply with stringent privacy laws, such as HIPAA, to ensure patient data is secure. Encryption tools, secure cloud storage, and restricted data access can safeguard patient information.
Accuracy and Reliability: Remote diagnostics must maintain a high level of accuracy. AI-powered tools, along with access to in-person care when needed, can help minimize the risk of misdiagnosis.
User-Friendly Platforms: Tele-ophthalmology platforms should be designed to be easy to use, even for patients who are not tech-savvy, particularly elderly patients.
6. The Future of Tele-Ophthalmology
With advancing technology, we can expect new diagnostic tools, increased AI integration, and a wider application of telemedicine in ophthalmology. Mobile telemedicine units, satellite connectivity, and mobile diagnostics are being deployed to reach underserved communities, helping bridge global disparities in eye health.
Conclusion
Telemedicine in ophthalmology is transforming how eye care is delivered, making it more convenient, affordable, and accessible. Tele-ophthalmology enables specialized care remotely, ensuring patients receive timely, appropriate treatment regardless of where they live. As technology evolves, tele-ophthalmology will play an even greater role in preventing vision loss and enhancing eye care outcomes worldwide.
